January 31, 2025/Midnight
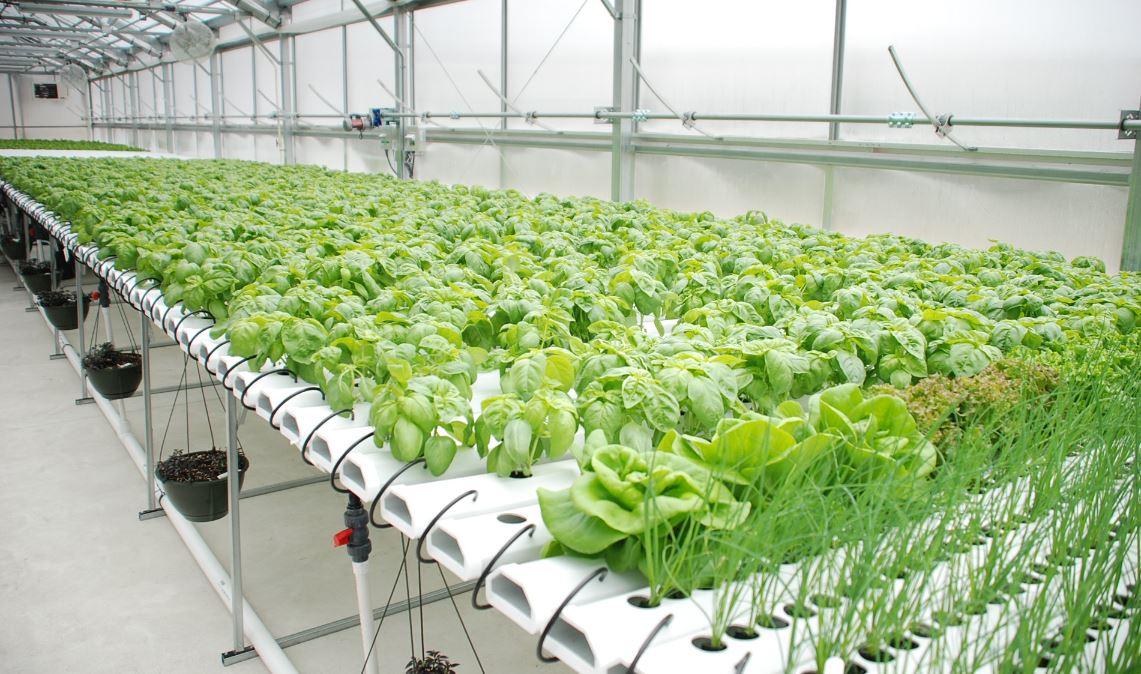
Erie, Pa. — In the face of rising global food demands and environmental challenges, the need for innovative farming solutions has never been greater. Hydroponic farming, which allows crops to grow without soil in nutrient–rich water solutions, is emerging as a game–changer for sustainable agriculture. At the forefront of this revolution are environmental scientists whose groundbreaking work in hydroponic technology sets new standards for efficiency and sustainability in urban farming.
What is Hydroponic Farming?
Hydroponic farming is an advanced agricultural technique that enables plants to grow using a nutrient solution instead of soil.By controlling the environment—temperature, humidity, light, and nutrient levels —farmers can produce crops with higher yields, faster growth rates, and lower environmental impact.
As an Environmental Science student at Gannon University, my own research focuses on enhancing hydroponic systems through advanced nutrient management, water recycling, and automation technologies. My work has helped to optimize water usage, reduce waste, and improve plant health in hydroponic farms across urban communities.
The U.S. Food Security Challenge
The U.S. is grappling with food security challenges, particularly in densely populated cities with limited space for traditional farming. According to recent reports, over 23.5 million Americans live in food deserts, where access to affordable, healthy food is scarce.
Hydroponics provides a viable solution to food insecurity. With minimal space requirements and controlled growing conditions, we can establish farms in urban areas and supply fresh produce directly to local communities.
Innovative hydroponic designs have been implemented in pilot projects across various states, demonstrating a 25% reduction in resource use and consistent year–round production regardless of climate conditions.
Environmental and Economic Advantages
Traditional farming methods contribute significantly to environmental degradation through deforestation, water waste, and chemical runoff. Hydroponic systems, however, provide a sustainable alternative by:
- Reducing water consumption through recirculating systems that use water more efficiently.
- Eliminating the need for chemical pesticides by using controlled environments to prevent pest infestations.
- Lowering carbon emissions by decreasing transportation distances between farms and consumers.
From an economic standpoint, hydroponics also offers business opportunities for urban entrepreneurs. By leveraging with advancements in hydroponic technology, urban farmers can operate cost–effective, high–yield farms within warehouses, shipping containers, and rooftop gardens.
Technology Meets Agriculture
One of the most exciting aspects of hydroponics is its intersection with technology. My research has introduced the use of IoT sensors and data analytics to monitor plant health, nutrient levels, and environmental conditions in real time. These smart systems help farmers make data–driven decisions, reducing resource waste and maximizing yields.
Additionally, my team is integrating AI–powered analytics to automate nutrient delivery further and optimize plant growth cycles.
The Road Ahead
Despite hydroponics’ promising future, challenges remain, such as initial setup costs and the need for skilled labor. However, experts are confident that ongoing research and investment will make hydroponic farming more accessible and affordable for communities nationwide.
As the U.S. continues addressing food security and environmental sustainability, hydroponics stands as a hope for a greener, healthier future. With innovators like graduate students at Gannon, leading the way, the dream of a sustainable, food–secure nation is closer than ever.